Emperor Blog
Emperor Asset Management is responsible for managing an international unit trust as well as USD and ZAR bundles on the EasyEquities platform. One of the factors driving international markets this year, is the re-appearance of inflation. Inflation is present in markets all around the world, however, this article focuses on inflation in the US market specifically as it gives us a good indication of what is happening globally.
Inflation is described as the decline of purchasing power of a given currency over a period of time. This decline in purchasing power is represented by an increase in the average price level of a basket of particular goods and services in an economy over a certain period of time. The basket particular of goods and services often includes commodities such as grains, metals, fuels, utilities such as electricity and transportation and services such as healthcare, entertainment and labour. This increase in the general level of prices is often expressed as a percentage and essentially indicates that one unit of currency buys less than it did in previous periods.
Investors worry about an inflation rate that is too high as it often has a negative impact on stocks. High inflation causes an increase in borrowing costs, an increase in input costs (i.e. material and labour) as well as reduces the standard of living. The most important impact on this market is that higher inflation reduces expectations of earnings growth, thereby putting downward pressure on stock prices. The stock market, however, anticipates a certain amount of inflation each year and adjusts what the expected returns should be against this expected inflation. But if inflation suddenly goes from 2% to 4% in a very short space of time for example, history indicates the overall market will react negatively, because investors will now be demanding a higher return to compensate for the now-higher level of risk, the result? A drop in stock prices.
The last time the US experienced slow growth and inflation that was at a record high was during the 1970s, with interest rates rising to around 20%, this phenomenon is more commonly referred to as stagflation. Since the economic expansion that began in the 1990s, inflation has remained relatively stable at around 3% or less. It is worthwhile noting that since 1996 the Fed has introduced monetary policy with the aim of keeping inflation at target rate of 2% , or at least seeks to achieve an inflation rate that averages 2% over time.
More recently, the increase in US inflation has been making headlines in many articles all across the US. The economy is slowly starting to return to normal, with some sectors booming following their reopening after the lifting of certain restrictions related to the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020. The most notable component is CPI, with the core CPI rising at a rate of 3.8% year-over-year, the highest pace since 1992.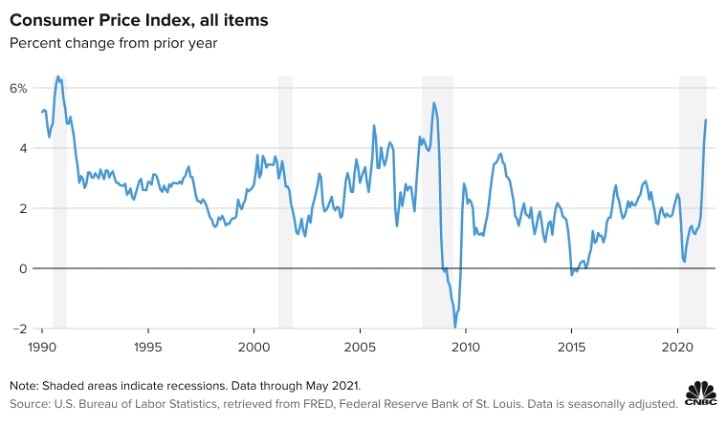
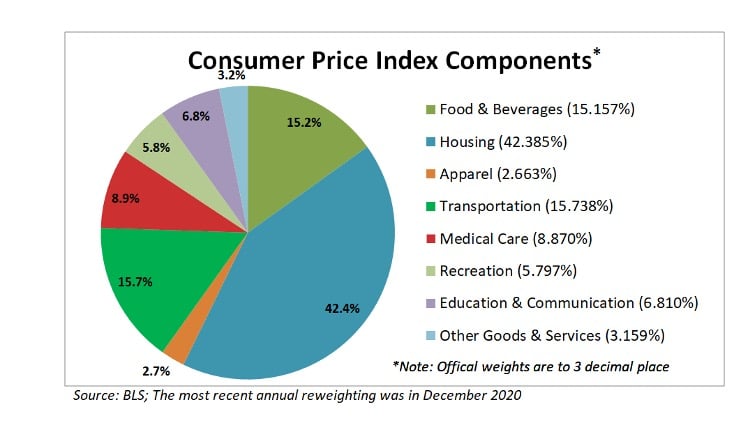
Other components attributable to the CPI that have also seen significant increases are shelter, which accounts for more than 30% of CPI. The shelter index rose 0.3% in May, and 2.2% over the last 12 months. The rent portion saw a rise of0.2%, and the index for owners’ equivalent rent — or the hypothetical amount a homeowner would charge someone to rent their dwelling — rose by 0.3%. Lodging away from home rose just 0.4%, after jumping 7.6% in April. Used car and truck prices surged 21% following a 10% increase in April alone. Lumber prices alone have risen 124% in 2021 amid persistent demand for building materials, many houses in the US are built from lumber, hence its impact on CPI. The price of certain metals has also exhibited a substantial increase with copper, which often seen as a proxy for economic activity, has jumped nearly 36%. Energy prices overall jumped 25% from a year earlier, including a 46% increase for gasoline and 37.3% for fuel oil. Another big component of CPI, is medical care, which fell 0.1% in June, after rising in the four previous months. Medical care prices rose just 0.9% over the past 12 months, the smallest increase since the period ending March 1941.
Several months of elevated price increases is expected due to pent-up demand and supply chain shortages, along with higher shipping costs. COVID-19 vaccinations, low interest rates and nearly $6 trillion in government relief since the pandemic started in the United States in March 2020 are fueling demand, and straining the supply chain. Much of the increase in inflation for the month of June was also driven by factors that are likely to subside in the coming months, such as the semiconductor chip shortage that is reducing the supply of automobiles and the post-reopening surge in consumer demand.
Many analysts view this surge in inflation as transitory (temporary), and are attributing it to a rise in prices centered in areas affected by the pandemic. However, it is worth noting that although inflation has likely reached its peak in June, it is expected to remain elevated through part of 2022, as prices for many travel-related services are still below pre-pandemic levels, and with nearly 160 million Americans immunized, demand for travel is picking up, as a result prices are expected to increase as the industry normalises once again.
We see the secular growth situation unchanged for now with real, net of inflation, long term rates remaining at lows thus supporting our portfolio thematic thesis. We at Emperor continue to monitor and analyse this situation and adjust our portfolio as necessary.
At Emperor, we believe that it is important for your investment to beat the inflation rate. Login to EasyEquities to view our products.
Happy Investing!

